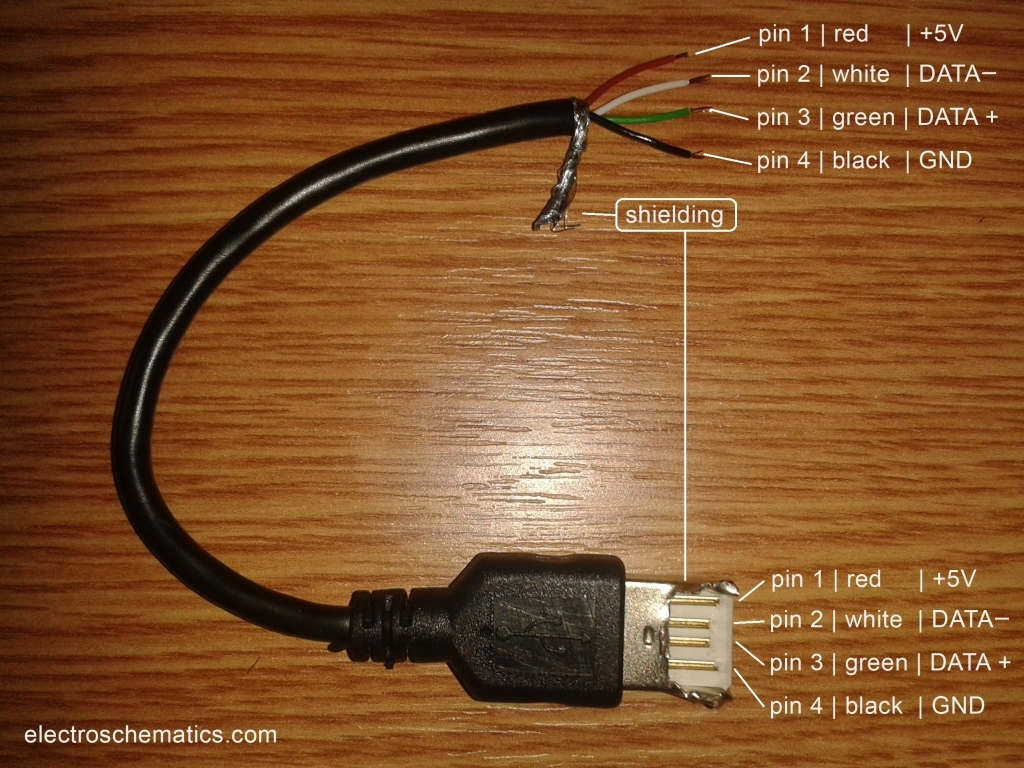
USB connectors are widely used in today’s digital world for connecting various devices to computers and other electronic devices. Understanding the wiring diagram of a USB connector is essential for troubleshooting connectivity issues and for DIY projects involving USB cables.
There are different types of USB connectors, such as Type-A, Type-B, Mini-USB, Micro-USB, and USB-C. Each type has its own pinout configuration and wiring diagram, which determines how data and power are transmitted through the connector.
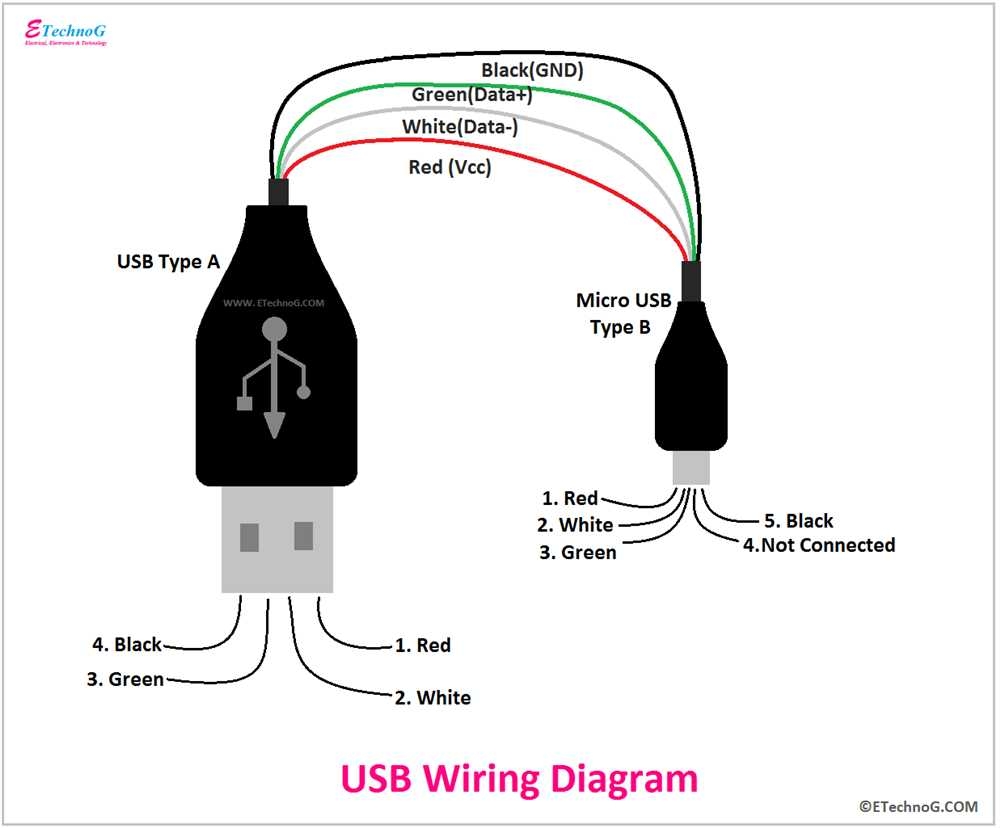 A Complete Guide To Wiring Diagrams For USB Plug Connections (stewart-switch.com)
A Complete Guide To Wiring Diagrams For USB Plug Connections (stewart-switch.com)
When looking at a USB connector wiring diagram, it is important to pay attention to the pinout configuration. The pins are typically labeled as VCC (power), D+ (data +), D- (data -), and GND (ground). Understanding which wire corresponds to each pin is crucial for proper connectivity.
In a USB Type-A connector, the pinout configuration is as follows: Pin 1 – VCC, Pin 2 – D-, Pin 3 – D+, and Pin 4 – GND. For Type-B connectors, the pinout configuration may vary depending on the specific type of connector.
It is important to note that improper wiring of a USB connector can lead to connectivity issues, data transfer errors, or even damage to the connected devices. When creating custom USB cables or adapters, it is recommended to follow a reliable wiring diagram to ensure proper functionality.
USB-C connectors, which are becoming more common in modern devices, have a reversible design and a different pinout configuration compared to traditional USB connectors. The wiring diagram for USB-C connectors typically includes pins for power delivery, data transmission, and audio/video output.
In conclusion, understanding the wiring diagram of a USB connector is crucial for ensuring proper connectivity and functionality of devices. Whether you are troubleshooting connectivity issues or working on a DIY project involving USB cables, having a good grasp of the pinout configuration is essential. By following a reliable wiring diagram, you can avoid potential issues and ensure seamless communication between devices.